Operations Maintenance
Development of school sanitation systems focuses resources more on design and build with little or no resources allocated for operations and maintenance, often with disastrous consequences.
Development of school sanitation systems focuses resources more on design and build with little or no resources allocated for operations and maintenance, often with disastrous consequences.
The efficiency and longevity (lifespan) of school sanitation facilities are determined by their operations and maintenance (O&M) regimen. Misuse, neglect and irregular maintenance can cause latrines to overflow, incur high renovation costs and cause disease outbreaks.
Unlike building and design, O&M gets little or no attention and is often the reason for the breakdown of the school sanitation systems.
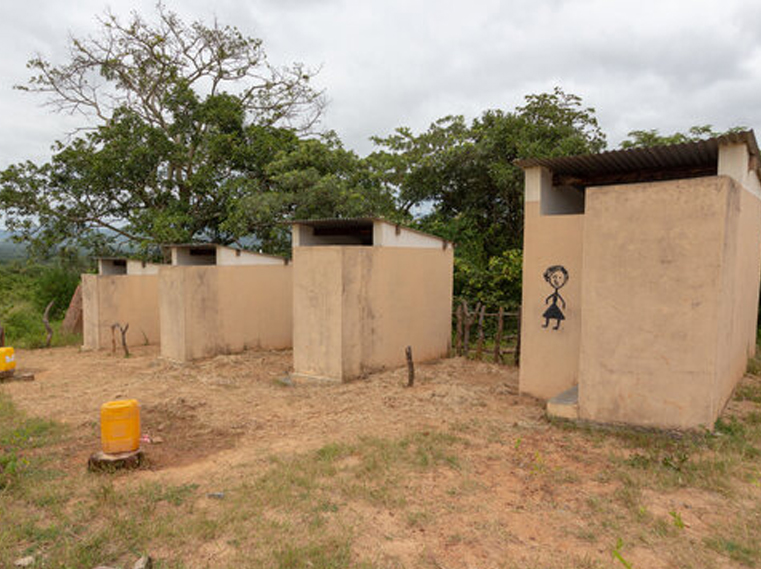
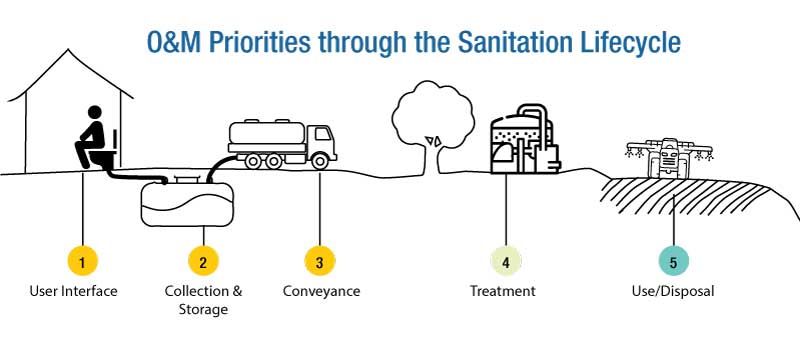

Poor O&M also arises from
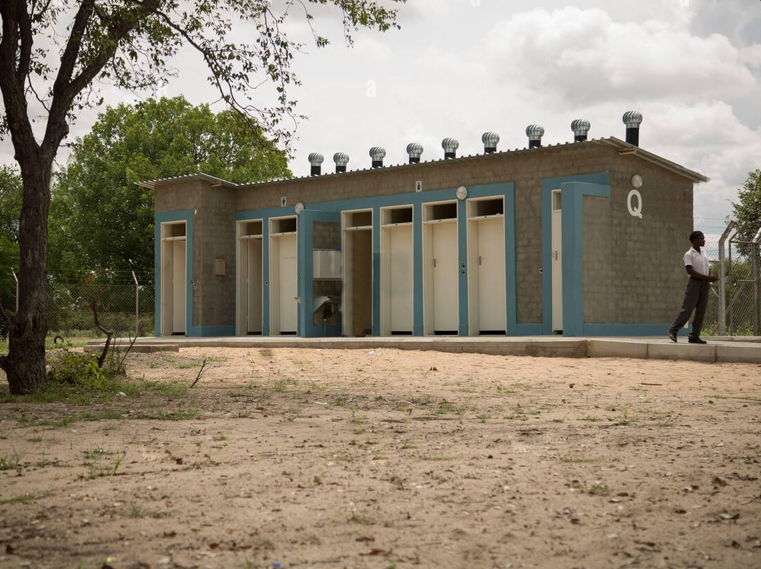

Sustainable O&M, however, requires careful planning and adequate resources to implement O&M. Who should fund sanitation O&M and how, receives far less attention than its design and construction (Sohail, 2001).
School sanitation O&M falls under the following categories;
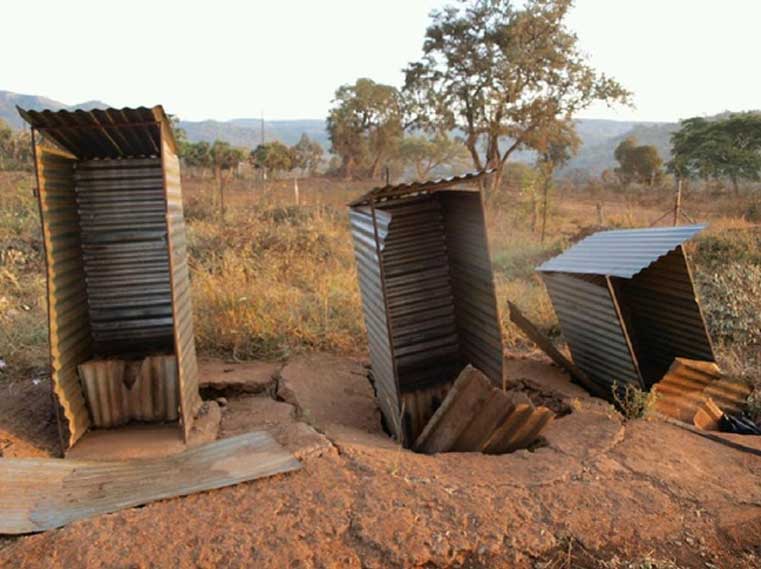

Public health and sanitation departments are usually charged with earmarking funds for O&M for public schools but with budget shortfalls, only a fraction of available funds are allocated for O&M.
Schools can raise funds for O&M (paying for cleaners and cleaning supplies) by engaging in revenue-generating activities like resource recovery. Schools can also raise revenue for O&M by charging parents a nominal fee for minor repairs of sanitation facilities. For instance, Kalungu High School in Uganda operates a successful O&M system by generating additional revenue from billing parents of students.
One other alternative is for schools to form a group to seek credit facilities to support O&M for major repairs, for instance, after a major weather event like a storm.